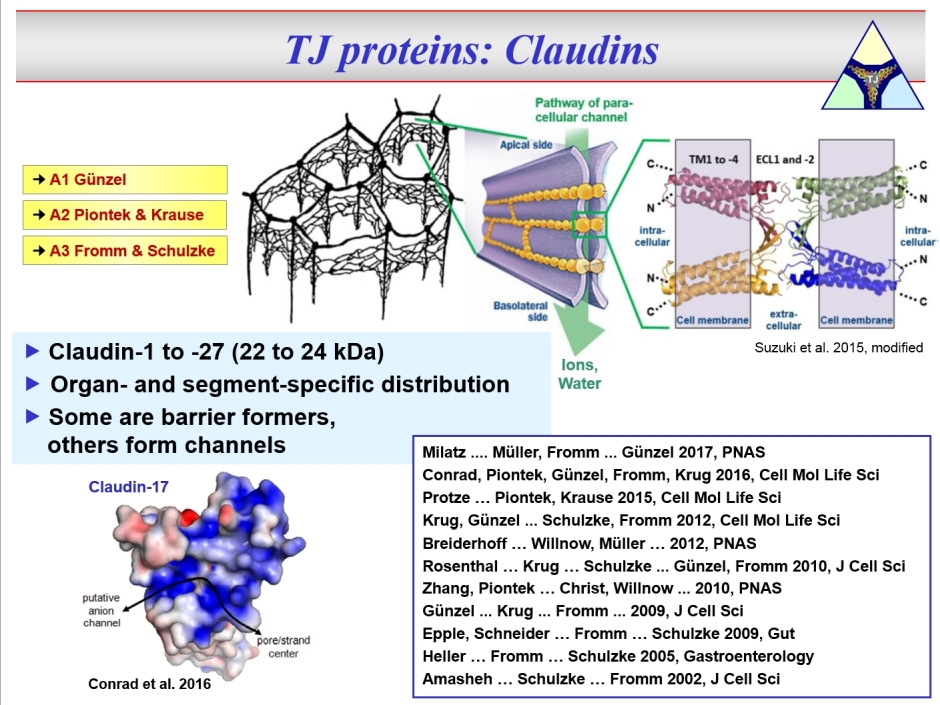
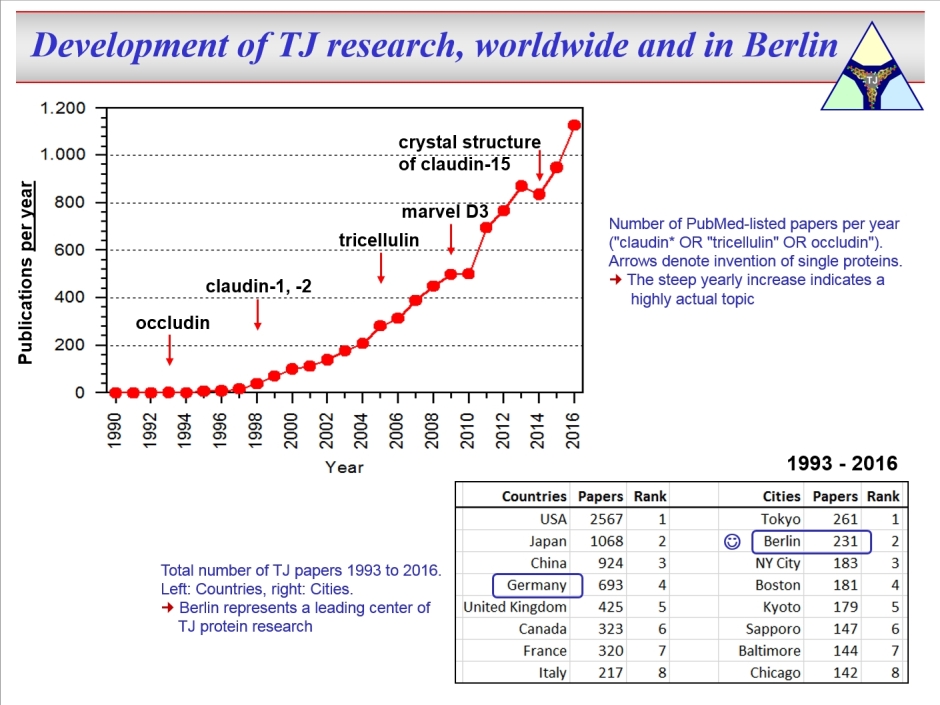
DFG Research Training Group "TJ-Train" (GRK 2318) That's all about: More detailed Publications of the doctoral students The tight junction (TJ) connects neighbouring epithelial or endothelial cells and is the central element of barrier function, as it controls paracellular passage of solutes and water. Whether the TJ simply increases tightness or selectively mediates permeability varies greatly in different tissues and is determined by the TJ protein composition. There are two families of TJ proteins, the claudins and the TAMPs. So far, 27 claudins were discovered in mammalia.
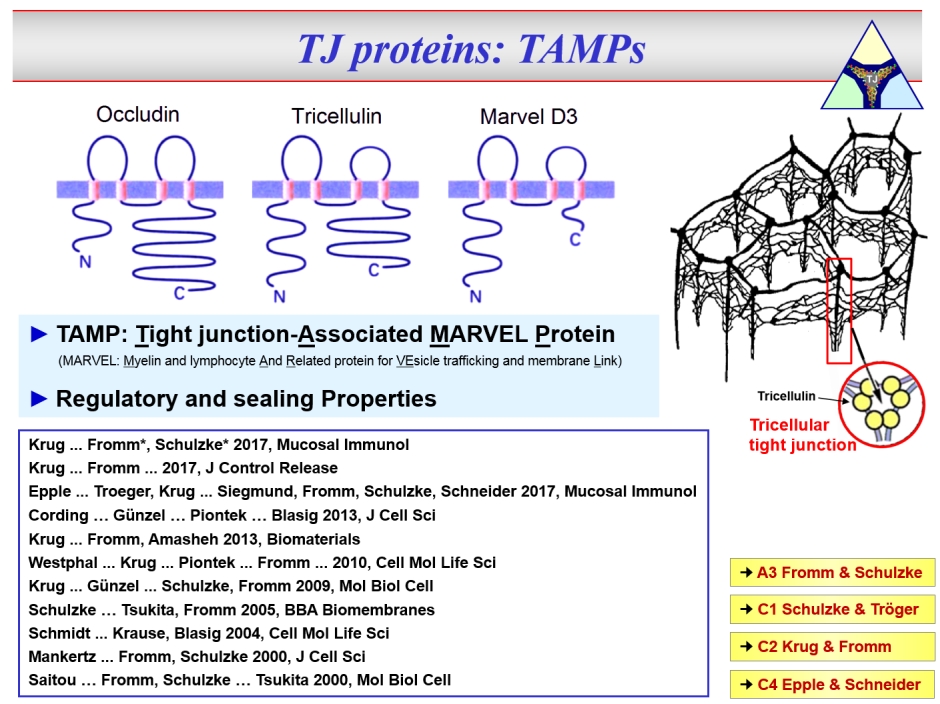
The second family of TJ proteins are the TAMPs, comprising Occludin, Tricellulin and Marvel D3.
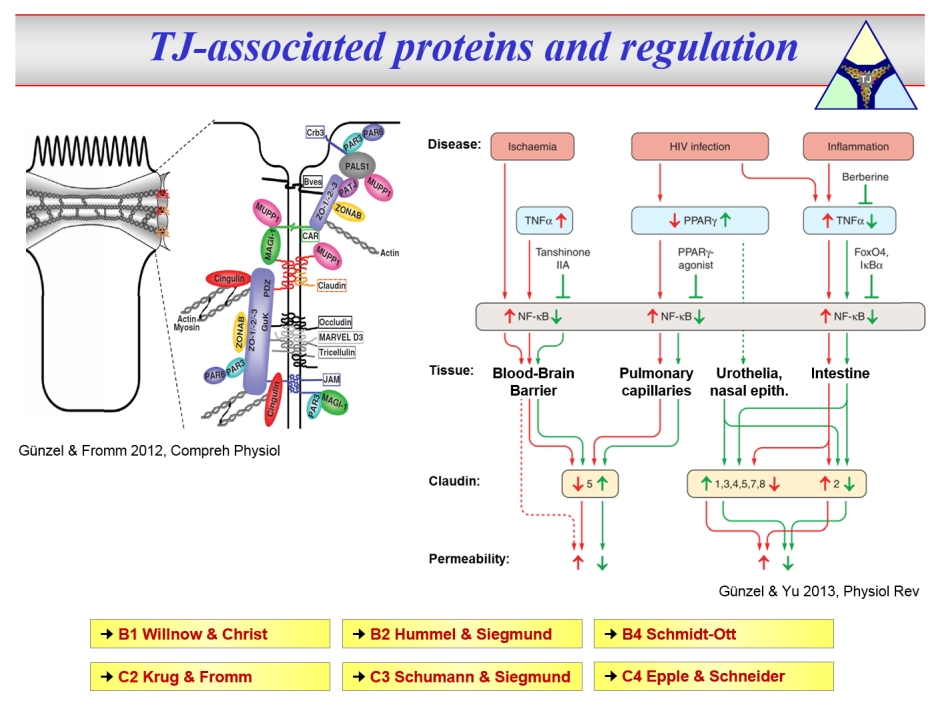
TJs underlie extensive extra- and intracellular signalling, but also regulate epithelial functions and cellular differentiation. Furthermore, numerous TJ proteins serve as receptors for certain pathogens.
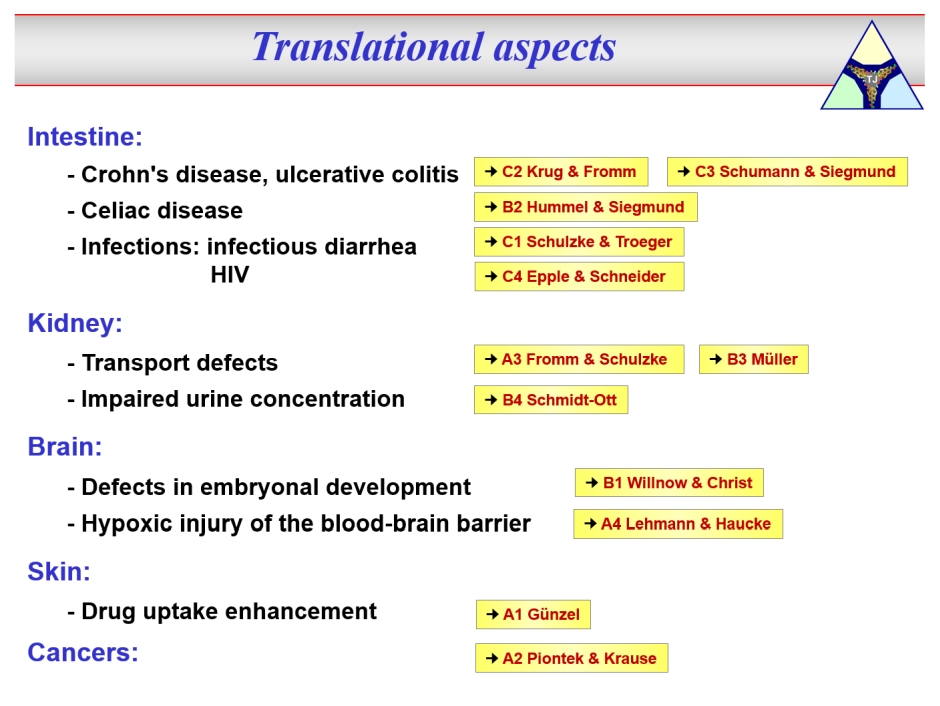
Thus, TJ proteins are involved in the pathogenesis of numerous diseases. Alterations in TJ composition and architecture may e.g. cause unwanted leak flux or antigen passage and may thus maintain disease activity or even directly trigger disease onset.
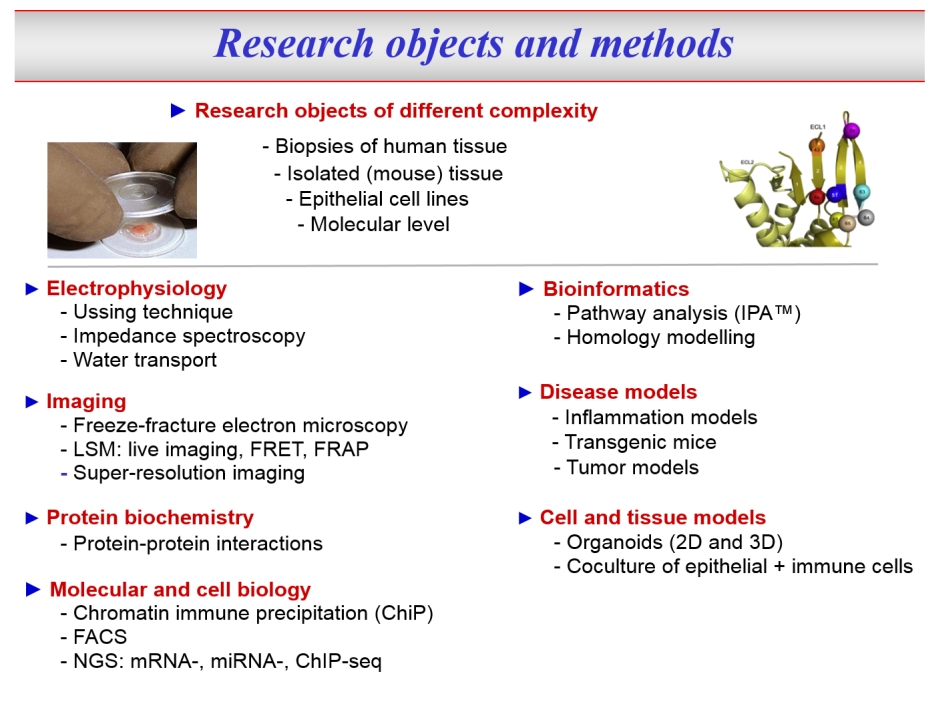
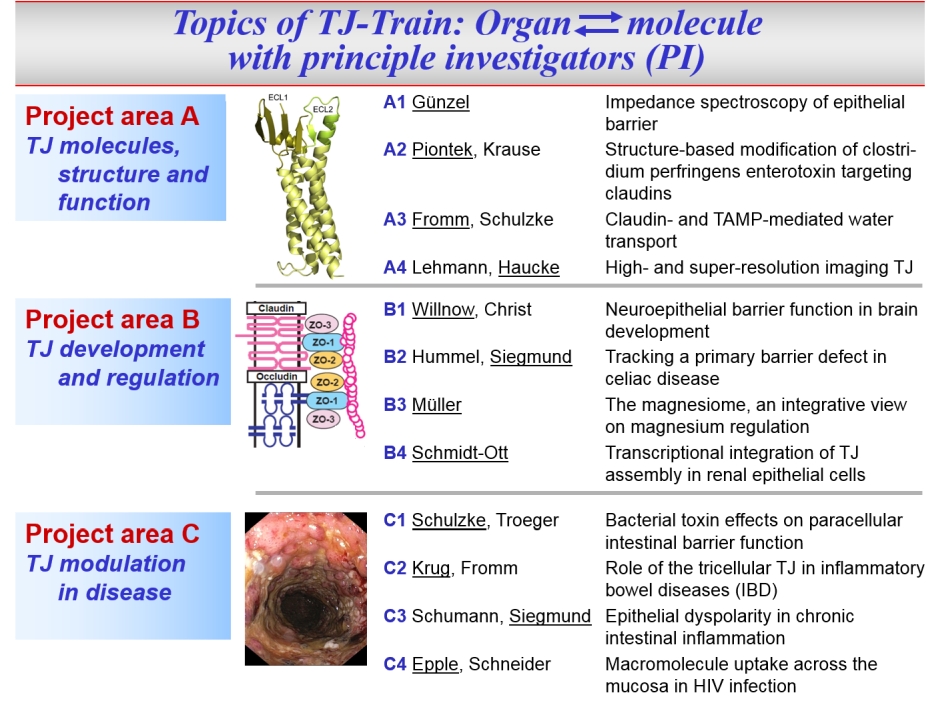
In this environment, our Research Training Group "TJ-Train" is located. Its aim is to train PhD and MD students together. On the one hand, the MD students will be introduced to basic science, and on the other hand the PhD students will be brought into contact with clinical aspects and objectives. Per cohort, 12 PhD and 12 MD students will be trained, PhDs for a period of 3 years, MDs for a period of 12 months. Thus, "TJ-Train" will not only qualify students for research and impart broad basic knowledge but will also particularly strengthen the transfer of knowledge between theoretical and clinical research and promote translational research approaches. Through the participating researchers and their working groups, all doctoral students will have access to a very wide range of methods (including modern molecular biological and electrophysiological techniques, biophysical and bioinformatics methods, super-resolution light microscopy, next generation sequencing), that will be applied to the analysis of cell culture models, animal models and human biopsies.
Review articles and editions for introduction into the field: Liebing E*, Krug SM* (*shared first authorship), Neurath MF, Siegmund B, Becker C (2024) Wall of resilience: How the intestinal epithelium prevents inflammatory onslaught in the gut. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18(#): ###### (## pages), doi:10.1016/j.jcmgh.2024.101423 (Review)Citi S, Fromm M, Furuse M, Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Nusrat A, Tsukita S, Turner JR (2024) A short guide to the tight junction. J. Cell Sci. 137(9): jcs261776 (12 pages), doi: 10.1242/jcs.261776 (Perspective, Review) Tsamo Tetou A, GŁnzel D (2024) The role of claudins in renal transepithelial transport and kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 33(#5): 535-542 (8 pages), doi: 10.1097/mnh.0000000000001003 (Review) Fromm M, Krug SM, eds. (2024) The tight junction and its proteins: From structure to pathologies. Special Issue of the Int. J. Mol. Sci., 14 articles: Collection (Edition) Meoli L, GŁnzel D (2023) The role of claudins in homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. (17 pages), doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00731-y (Review) Meoli L, GŁnzel D (2020) Channel functions of claudins in the organization of biological systems. BBA - Biomembranes 1862(9): 183344 (18 pages) [PubMed] [WebPage] [PDF] [Supplementary Fig. S1] (Review) Piontek J, Krug SM, Protze J, Krause G, Fromm M (2020) Molecular architecture and assembly of the tight junction backbone. BBA - Biomembranes 1862(7): 183279 (15 pages) [PubMed] [WebPage] [PDF] [Supplement] (Review) Fromm M, Krug SM, eds. (2020) The tight junction and Its proteins: More than just a barrier, Special Issue of the Int. J. Mol. Sci., 44 articles: Collection (Edition) GŁnzel D, Yu AS (2013) Claudins and the modulation of tight junction permeability. Physiol. Rev. 93(2): 525-569 [PubMed] [WebPage] [PDF] (Review) GŁnzel D, Fromm M (2012) Claudins and other tight junction proteins. Compreh. Physiol. (former Handbook of Physiology) 2(3): 1819-1852 [PubMed] [WebPage] [PDF] (Review) All publications of the Clinical Physiology / Nutritional Medicine: Here |